Direct vs Indirect Cash Flow 101: Key Difference Between Cash Flow Methods
However, it lacks detailed insights into specific cash transactions and their sources, which means you might miss important information about your finances. There are two methods to prepare the cash flow statement (direct and indirect). Both methods tell the same story about how cash moves around in the business, but from different perspectives.
Failing to account for these the difference between the direct and indirect cash flow methods timing differences in cash flow statements can create discrepancies in reporting, leading to incorrect projections of available cash. Then, it adjusts for cash flows, considering receivables, payables, and more. This includes looking at non-cash transactions that affect finances, from accrued revenues to prepaid expenses.
Companies tend to use the indirect method more often than the direct method. It’s much easier for a finance team to assemble because it uses information obtained directly from the balance sheet and income statement. The indirect method also considers accruals, so all receivable transactions, including billing and invoicing, are part of the indirect cash flow statement. Businesses may prefer the direct method for its clarity and transparency, as it provides a detailed account of actual cash received and spent, which is particularly useful for internal management. This method is ideal for businesses that deal primarily in cash transactions, such as small retail or service-oriented businesses. The direct method can offer a more tangible and immediate understanding of cash flow, which is helpful for daily operational decisions and financial planning.
Direct Cash Flow Statement
Conversely, if accounts payable increased, it indicates that expenses were incurred without cash payment. Cash flow, in the context of business finance, refers to the net amount of cash and cash-equivalents that move into and out of a company. Essentially, cash flow gives a snapshot of a company’s liquidity and its efficiency at generating and using cash. Many businesses focus heavily on operating and investing activities while overlooking cash flows related to financing.
- Despite this, its ability to bridge accrual accounting with cash realities makes it valuable for comprehensive financial analysis and it’s favored by external stakeholders such as investors and banks.
- Automated cash flow statements let you focus on strategic forecasting and decision-making, confident that your financial statements are accurate and up to date.
- As a result, the indirect method is often preferred by companies that want to save time and resources while still having a good understanding of their cash movements.
- These requirements became effective in 1988 and, while the standard now has the title of ASC 230, remain effective today.
Why Manual AR in Heavy Industries Threatens Financial Stability
With this, the direct and indirect methods respectively offer different perspectives on cash flow calculation. The indirect method might not accurately represent the company’s current cash position. It indirectly calculates net cash flow from other financial statements, meaning the numbers might not be up to date if the previous financial statements aren’t accurate or updated. This could lead to misleading information about the company’s cash situation. Unlike the direct method, the indirect method provides less detailed information about specific cash flow activities. It doesn’t offer a deep understanding of what contributes to the company’s net cash flows.
Ways to improve your cash flow forecasting process
- Automating some of your processes can help you improve your accounting processes, ensure accuracy, and get more insight into cash flows.
- The direct method focuses primarily on operating activities because these represent your business’s core cash-generating activities.
- The direct method sheds light on cash transactions, aiding operational and cash flow forecasts.
- Companies need to think about what they have and what they want to achieve.
On the other hand, the indirect method starts with net income and adjusts for non-cash transactions and changes in working capital, providing a bridge between your accrual accounting and cash reality. The goal of cash flow reporting is to simplify complex financial data. The indirect cash flow method is great for integrating cash flow operations with financial reporting.
Which is Best For Your Business?
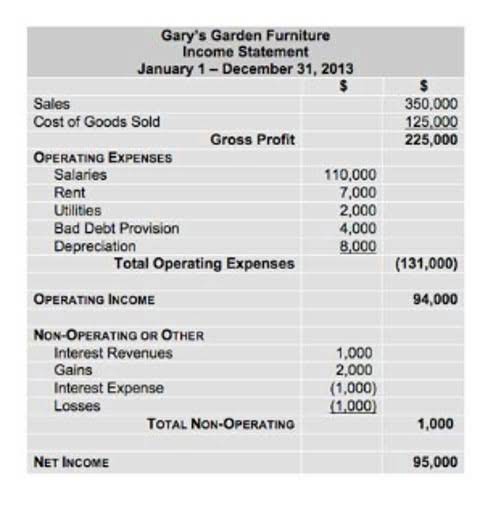
Since most large companies use accrual accounting, most also use the indirect method of cash flow accounting. Typically, as a company grows, it becomes increasingly difficult to use the direct method of cash flow accounting. Based on accrual accounting, this method incorporates non-operating expenses such as accounts payable and depreciation into the cash flow equation. As such, one advantage of the indirect method is that you don’t have to do an extra calculation to convert net income to the cash provided by operating activities, as you do with the direct method.
Opting for the indirect method might be the right choice if you’re seeking streamlined and efficient cash flow reporting, as it builds upon the net income and adjusts for non-cash items. It’s particularly suitable for larger corporations with intricate operations, as it offers a summarized perspective that might be easier to manage. Working capital encompasses current assets and liabilities that impact operations. Changes in items like accounts receivable, inventory, accounts payable, etc., need adjustment. For instance, if accounts receivable increase during a period, it means sales were made on credit, and cash wasn’t collected yet.
Enerpize integrates with your bank accounts, automatically syncing your transactions to give you up-to-date insights into your cash flow situation. Its detailed reports highlight key trends, enabling you to identify patterns, assess liquidity, and track cash flow from operations, all in one place. Whether you’re managing accounts payable, accounts receivable, or preparing for taxes, Enerpize streamlines these processes and ensures you stay organized and compliant.
Direct cash flow reporting takes a long time to prepare because most businesses work on an accrual basis. Under the indirect method, the cash flows statement will present net income on the first line. The following lines will show increases and decreases in asset and liability accounts, and these items will be added to or subtracted from net income based on the cash impact of the item.